
Computers are usually used to calculate Fourier transforms of anything but the simplest signals. An example of this is a filter which blocks high frequencies.Ĭalculating a Fourier transform requires understanding of integration and imaginary numbers. Many systems do different things to different frequencies, so these kinds of systems can be described by what they do to each frequency. In the audio example above, looking at the signal with respect to time does not make it obvious that the notes A, B, and C are in the signal.
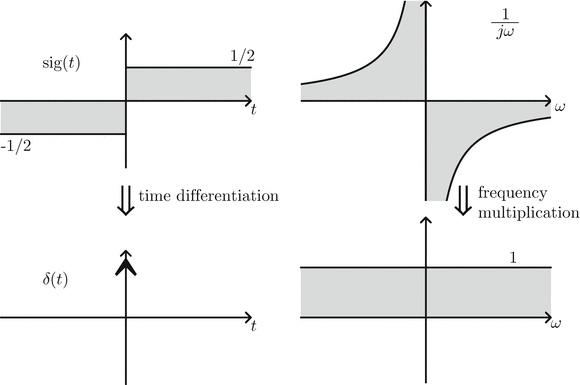
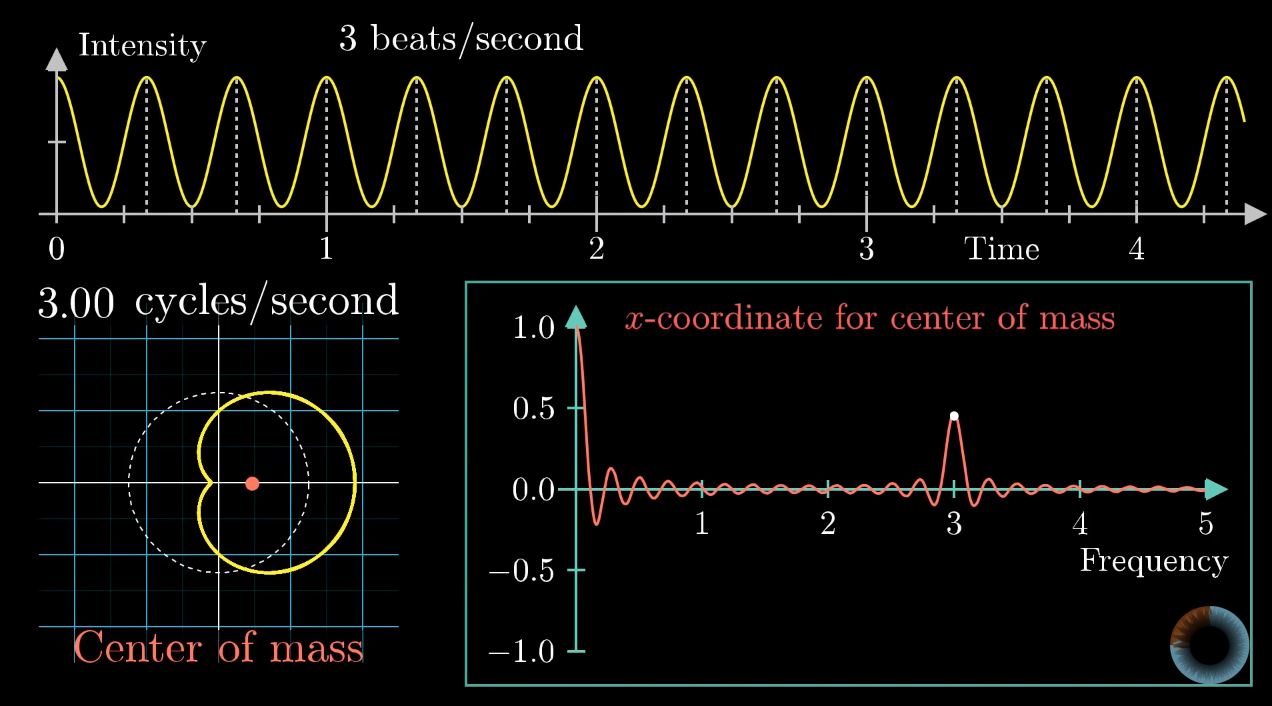
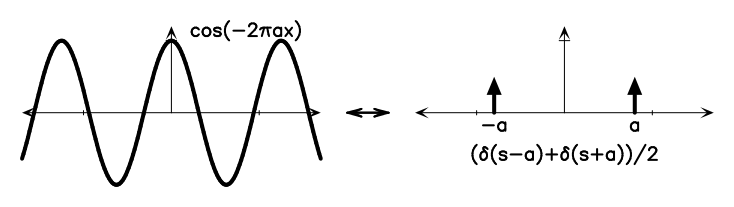
The Fourier transform plots the amplitudes and phases of these cosines and sines against their respective frequencies.įourier transforms are important, because many signals make more sense when their frequencies are separated. Many signals can be created by adding cosines and sines together with varying amplitudes and frequencies. Making a graph of the Fourier transform of this sound wave (with the frequency on the x-axis and the intensity on the y-axis) will show a peak at each frequency which corresponds with one of the musical notes. For example, consider a sound wave which contains three different musical notes: A, B, and C. The Fourier transform of a function f ( x ) Ī Fourier transform shows what frequencies are in a signal. This function has many uses in cryptography, oceanography, machine learning, radiology, quantum physics as well as sound design and visualization. Discrete Fourier transforms and their inverses can be computed quickly using the FFT algorithm, especially when N is highly composite that is, it can be. The output of a Fourier transform is sometimes called a frequency spectrum or distribution because it displays a distribution of possible frequencies of the input. A Fourier transform takes this complex wave and is able to find the frequencies that made it, meaning it can find the notes that a chord is made from. This works because each of the different note's waves interfere with each other by adding together or canceling out at different points in the wave. When played, the sounds of the notes of the chord mix together and form a sound wave. The Fourier transform is a mathematical function that can be used to find the base frequencies that a wave is made of. Fourier analysis grew from the study of Fourier series, and is named after Joseph. In mathematics, Fourier analysis ( / frie, - ir /) 1 is the study of the way general functions may be represented or approximated by sums of simpler trigonometric functions. The output of the transform is a complex -valued function of frequency. So far, we have concentrated on the discrete Fourier transform. You can help Wikipedia by reading Wikipedia:How to write Simple English pages, then simplifying the article. Fourier analysis reveals the oscillatory components of signals and functions. In physics and mathematics, the Fourier transform ( FT) is a transform that converts a function into a form that describes the frequencies present in the original function. On the contrary, the tail is a high frequency area because the pixel intensity shows a rapid alternation between the hair and the background.The English used in this article or section may not be easy for everybody to understand. In the figure above, the gray background behind the squirrel is a low frequency area because the intensities of the pixels slowly evolve from one pixel to another. In other words, the Fourier transform of a convolution of two functions is the product of their Fourier transforms. The Fourier transform is the mathematical operation that maps our signal in the temporal or spatial domain to a function in the frequency domain. The low frequencies are located in the center of the image, and the high frequencies near the boundaries. The amplitude and phase represent the distribution of energy in the frequency plane. (an histogram transformation has been applied). The amplitude is shown with a logarithmic scale to distinguish clearly the details That is why we will show the amplitude (modulus) and phase (argument) of the DFT separately, as in Fig.

In consequence, the DFT of an image is possibly complex, so it cannot be displayed with a single image. Note that the definition of the Fourier transform uses a complex exponential. Sobel and Canny detectors + Harris detector + Hough transformį(u,v) = \sum_ = F\).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
